In this article discussed about the VMware Virtual Machine and Some Virtual Machine features.
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) is a high-performance cluster file system (CFS) that provides storage virtualization optimized for virtual machines. Virtual machines consist of small sets of files which are managed by VMFS via physical disks and partitions. VMFS allows multiple vSphere hosts to share a clustered pool of storage among virtual machines.
Benefits of Virtual Machine File System (VMFS)
- Automated file system with hierarchical directory structure
- Optimization for virtual machines in a clustered environment
- CFS is journal logging for fast recovery.
- Encapsulation of the entire virtual machine state in a single directory
- Simplified provisioning and administration of virtual machines
VMware Virtual Machine Snapshots in the vSphere Environment
- VMware Virtual Machine Snapshot preserves the state and data of the virtual machine at a specific point of time.
- The state includes the virtual machine’s power states like powered-on, powered-off, suspended etc.
- Data includes all the files that make up a virtual machine, including disks, memory, and other devices.
- If at all the original VM goes down, we can always revert back to the latest snapshot and resume.
- virtual machine provides several operations for creating and managing snapshots and snapshots chain.
- Snapshots can be created, reverted back to any previous snapshot, and removed.
- Snapshot will usually be taken before you test a patch, software update or other change.
- Total of 32 snapshots can be taken for one virtual machine. But we limit the number to 2/3 because, snapshots start consuming the memory leading to decrease in performance.
- Snapshots should not be used as backups because, they do not suffice as a data protection and recovery method because snapshot files are just change of logs of the parent virtual disk.
- There are two types of snapshots that can be taken.
- Snapshot with memory: When we choose to take a snapshot with memory, a dump of internal state of the Virtual Machine is included in the snapshot. At the time of reverting back to the snapshot, the Virtual Machine will be in the powered-on state.
- Snapshot without memory: When we choose to take a snapshot without memory, the live state of the Virtual Machine and the internal memory won’t be captured. At the time of reverting back to the snapshot, the Virtual Machine will be in the powered-off state.
There is another option called Quiesce file system while taking a snapshot. This option is to make an application aware snapshot to preserve data consistency if writing operations are running on the Virtual Machine.
Managing VM Templates:
- A VMware Virtual Machine Template is the master copy image of the original virtual machines which includes virtual machines disks, virtual devices, and settings. It can be used as many times needed for the purpose of generating many virtual machines with same configurations and applications.
- We cannot power on or edit the template once it has been created. If at all we want to edit the template, we need to convert the template to a virtual machine, edit it and then convert back the Virtual Machine to a new template.
- Template approach provides greater security for virtual machine Cloning, and they are helpful in deploying high number of similar virtual machines since they preserve the virtual machine consistency.
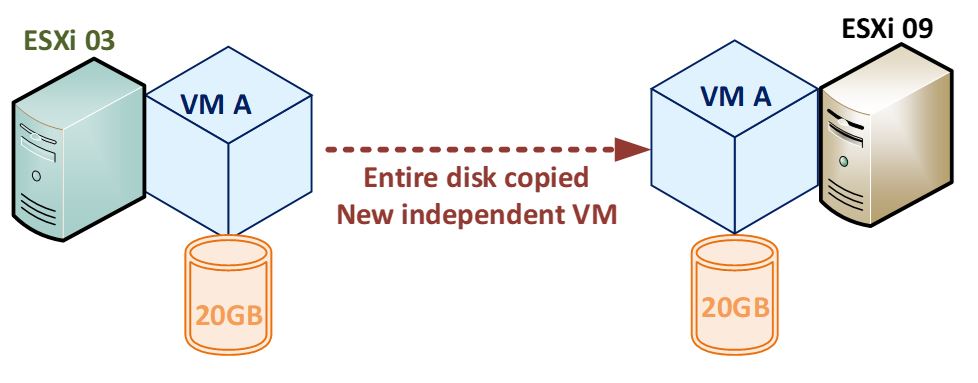
Clone a Virtual Machine
- A virtual machine Clone is the copy or replica of the original Virtual Machine. The existing Virtual Machine is called a parent, and the new cloned virtual machine is called a child. After cloning, the cloned virtual machines act as separate virtual machines. Clone a Template to a Template
- Using clone, we can perform installation and configuration once and then use the clone as basis for many future virtual machines.
- There are two types of clones –
- Full Clone
This type of clone is a complete separate copy of the VM that shares no system resources with the parents once it’s up and running. This kind of cloned VM generally has the faster performance.
- Linked Clone
This type of clone continues to share virtual disks with the parents after it’s created, up and running.
vSphere Fault Tolerance
Fault Tolerance (FT) in vSphere prevents data loss and downtime by creating a live shadow instance of a virtual machine (VM). Which means, if there is a cloned VM with same ip as the primary VM, then we need to enable FT for the cloned VM.
when there is a request coming for the ip address and both the addresses are active, the primary virtual machine will respond to the requests as long as it is in good state. The cloned virtual machine with vSphere Fault Tolerance enabled will just receive the request and produce no outgoing.
But once, the primary virtual machine is down, the cloned virtual machine starts replying to the requests from the customer. Once the primary virtual machine is up and working, the cloned VMware Virtual Machine will stop the outgoing by isolating the requests and resumes its recording feature.
Conclusion:
In this article described about VMware Virtual Machine functionality and features. In my previous article discussed about VMware fundamentals.
Please leave a comment if you have any questions.