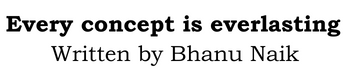The following procedure is Recover root password in Linux will assist you in changing (or) break your Linux root password in Red Hat Enterprise Linux or Community ENTerprise Operating System (CentOS) or resetting the password.
When you haven’t logged in as your root user for a long time, you’re more likely to encounter this issue.
In Linux, root privileges are associated with an account that has full access to all files, applications, and system functionalities.
Check Basic information about users and groups in RHEL/CENTOS.
My root password was lost, now will reset it.
How to Recover Root Password in Linux
Step1: My machine is running on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.5. First reboot the machine, as soon as you press any arrow key the system STOP the booting process.
Observer below screenshot ,2 options are existing.
- Boot with default kernel.
- Booting into Rescue Mode is used for repair purpose, but it requires root password.
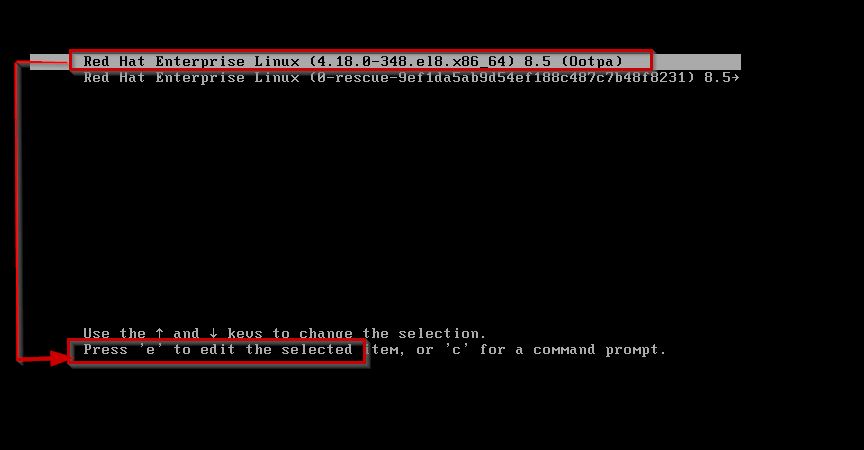
So, select default kernel line Red Hat Enterprise Linux (4.18.0-348.el8.x86_64) 8.5 (Ootpa) and at the bottom you see press e to edit the selected line.
It opens the parameters kernel, here you can see a word called linux ,the name of the kernel is vmlinuz .
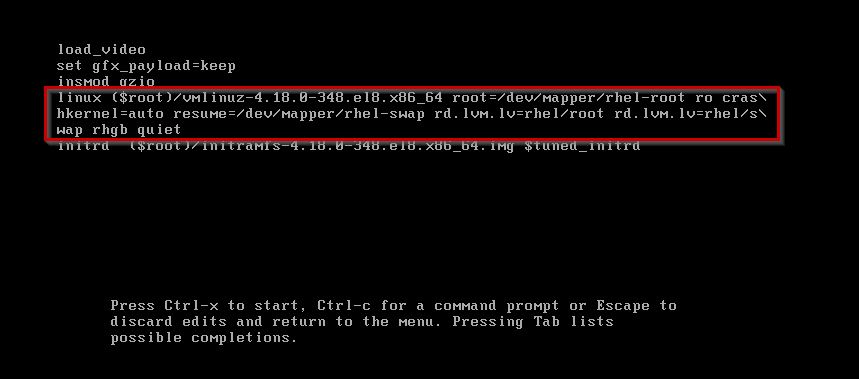
Step2: you have to come at end of the line using ctrl+e ,and type a kernel parameter called rd.break.
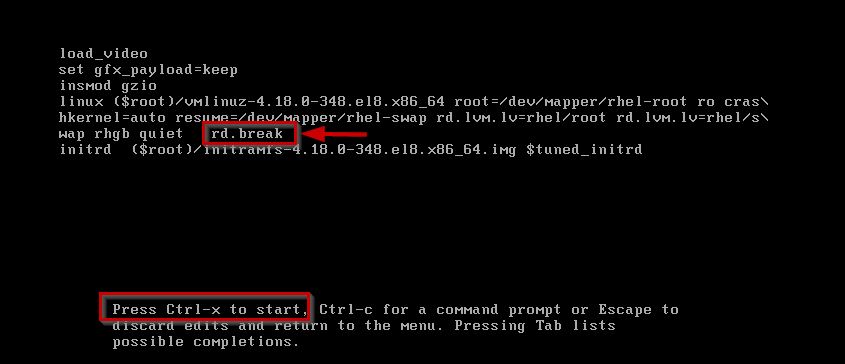
This process will be breaking the booting process and you will be taken to emergency mode.
Use ctrl+x to start with the kernel parameter.
The below image show entering emergency mode. I want to access my operating system through emergency mode.
Until operating system boots, files will be kept in /sysroot. Once the system is booted it will shift to /
During boot, operating system will be found in /sysroot, which is available in read-only mode. Hence, we can’t make the change.
So therefore, change the mode from Read Only to Read Write as shown below.

Step3: Use the chroot command to enter into Operating System, change the root password.
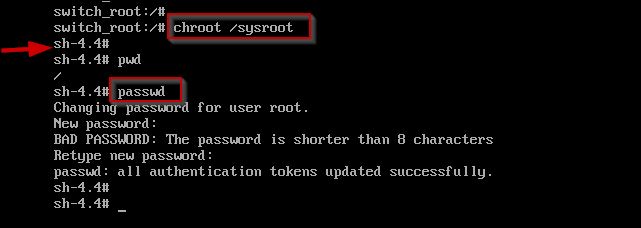
Step4: As a security measure, these changes must be update to SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux).
we need to create a hidden file with a name called .autorelabel. When you create such a file, the SELinux policy will be restored automatically at booting time.
touch /.autorelabel

As soon as the policies are re-enabled, the file will be deleted automatically.
Step5: The newly created root password can now be used to log in as the root user.
Recover root password in Linux Overview:
- Using rescue mode, the Red Hat Enterprise Linux environment can be booted entirely from a CD-ROM, or other boot device instead of from the system hard drive.
- Linux kernel image that are compressed, referred to as vmlinuz can be used to boot the system and load the kernel into memory.
- Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is an access control system which is in-built in the Linux kernel.
- With SELinux, you can enforce resource policies that identify how much access users, programs, and services have to resources on your computer.
- touch /. autorelabel command will create a hidden file under the root directory. On the next boot, the SELinux subsystem will detect that hidden file, and then relabel all of the files on that system with the exact SELinux contexts.
BIOS and Boot Loader Security:
The BIOS (basic input/output system) or BIOS equivalent and boot loader can be password protected in order to prevent unauthorized users from booting using removable media or obtaining root privileges. To prevent such attacks however, security measures need to be taken both according to the information the workstation holds and its location.
→ When the system is booted into single user mode, attackers gain automatic access as root without being prompted for their password, therefore prevent access to Single User Mode.
→ By using the GRUB editor interface, an attacker can change GRUB’s configuration or gain information about a machine that uses GRUB as its boot loader therefore prevent access to the GRUB Console.
→Dual-booting systems allow attackers to select an operating system, such as DOS, that ignores access controls and file permissions therefore prevent access to Non-Secure Operating Systems.
Conclusion:
Successfully rest the root password in RHEL machine. Above procedure is same for CENTOS machines as well.
Recover root password in Linux machines has been explained in standard procedure.
As a part of security, in order to prevent unauthorized access to the system, we require grub to be password protected