The purpose of this article to provide information about VMware vSphere 8.0. The exciting new features and enhancements that are available in vSphere 8 plus how they will improve operational efficiency, elevate security, and lead to more powerful workloads.
VMware has announced the release date of VMware vSphere 8.0 for the general public on August 30, 2022.
Data Processing Unit (DPU)
In VMware vSphere 8.0 ,the data processing unit exist today lives in the hardware layer and similar to any PCI device like a GPU. And a DPU contains compute, storage, memory, and some network interfaces.
Essentially in vSphere 8, we are putting an additional instance of ESXi directly on the DPU itself. And this allows us to offload ESXi services starting with some network and security services from NSX directly on to the DPU. vSphere 8 will support Greenfield installation with support for network offloading with NSX.
VMware vSphere with Tanzu
vSphere with Tanzu was introduced in vSphere 7 and with that improved Tanzu Kubernetes Grid or TKG.
In vSphere 8 more consolidating different Tanzu Kubernetes Grid runtimes into a single unified Kubernetes runtime. So, it will be the same runtime used for deploying Kubernetes on vSphere clusters, public clouds, private clouds.
There is also a new vSphere 8 feature called vSphere zones, this is used to isolate workloads across vSphere clusters.
Below diagram shows how vSphere zones look like in an environment. It allows our supervisor clusters and Tanzu Kubernetes clusters to span multiple vSphere clusters for increased availability. The vSphere namespace will also span the vSphere zones to support Tanzu Kubernetes clusters being deployed again for increased availability and maximum compute consumption.
Three vSphere zones are required for availability. During workload management activation, we will have the choice to deploy across vSphere zone or deploy to the single cluster option that available in VMware vSphere 8.0.
Cluster Class is an open specification that is part of the cluster API project. Cluster API finds the declarative way to lifecycle management Kubernetes clusters trough an existing management cluster. Cluster Class provides the declarative way to define the Kubernetes cluster configuration but now that also includes the default installed packages.
A Pinniped integration for Supervisor clusters and Tanzu Kubernetes clusters is now available. Configuring vCenter Single Sign-On in Supervisor clusters and Tanzu Kubernetes clusters allows direct access to OIDC identity providers.
Baseline lifecycle management or Update Manager is deprecated in vSphere 8. This means that the baseline lifecycle management is still supported in vSphere 8 and will be supported for lifecycle of vSphere 8. But VMware vSphere 8.0 will be the last release that supports baseline lifecycle management.
Staging is coming back to vSphere lifecycle manager. This allows vSphere lifecycle manager to pre-stage the update payloads down to the ESXi hosts in a cluster.
It reduces the overall remediation time and time spent in maintenance mode.
Less risk of remediation failure from live image transfer. Firmware payloads staged with Hardware Support Manager integration.
Parallel Remediation:
It allows to remediate multiple hosts in parallel. This will reduce the overall lifecycle time of a cluster. vSphere administrator decides how many hosts will be remediated in parallel by placing the desired hosts into maintenance mode.
Enhanced Recovery of vCenter
For lifecycle management or backup and restore Distributed Key-Value Store (DKVS) is introduced onto the ESXi hosts themselves. And this is going to be involved keeping the cluster stage and reconciling that information with vCenter.
vSphere Configuration Profile
This is next generation cluster configuration management and will be an eventual replacement for host profiles and host profiles continue to still be supported in vSphere 8.
The end goal of the vSphere Configuration Profiles is pretty much the same as host profiles to apply a cluster-wide configuration.
Enhancements in the Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning
Device Groups
The devices are grouped in the hardware layer and can be presented with a single unit to the virtual machine. They share a common PCIe switch or a direct interconnect.
Device Virtualization Extensions (DVX)
It involved in virtual machines that are consuming physical hardware devices. So, it doesn’t have to be limited AI/ML workloads that is consuming a physical hardware device. In previous releases VMs consuming physical hardware devices using direct device path I/O or dynamic direct path I/O will be limited in their mobility. So, we couldn’t do vMotion, suspend & resume the VM, and we couldn’t do Snapshots.
We loss some of the virtualization benefits when you are consuming physical hardware using direct path I/O.
Now device personalization extension builds on dynamic direct path I/O and introduces new framework in API, so that vendors can create new hardware backed virtual devices that does allow those virtualization features such as migration, suspend, resume, and Snapshots.
It means a new device driver will be developed on the ESXi host and for the VM.
Enhancements in the Guest OS & Workloads
Virtual Hardware Version 20: This allows for some compute maximum features and unlocks other features.
Virtual TPM Provisioning Policy
It is primarily created towards helping deploy Windows 11 workloads, but it could be applied to any workloads or any operating systems, that is leveraging a virtual TPM device.
When you are cloning a VM with a vTPM device that can introduce some security risks because the TPM secrets are also cloned. So, it opens some potential cross contaminations.
If we are doing a one-to-one clone, the virtual machine is using features like Windows BitLocker, Windows Hello, these features use TPM backed secrets. If you do replace the TPM device, in those instances.
Migration aware applications
VMware is making application or supporting applications to make them migration aware to vMotion notifications. There are certain applications that cannot tolerate vMotion like Voice over IP application could result in calls getting dropped.
In this case, ESXi will send a notification to VM when a vMotion event has been triggered and using VMware choose within the guest operating system, the application can intercept the notification and be told the vMotion event has been triggered and the application can perform some work, this could be anything like stopping services to gracefully failing over.
Once application has performed what it needs to do, it acknowledges the notification and allow the vMotion to complete. If the application does not respond within the defined timeout, the vMotion is going to happen regardless.
And other important aspect to be aware of, when you are using vMotion notifications and they are turned on for a particular virtual machine, these virtual machines automatically excluded from automatic DRS load balancing migrations. So, we still be able to manually migrate a virtual machine, still be able to put the host in maintenance mode and VM will be automatically migrated but for runtime DRS automatic load balancing, these VMs can be excluded.
High latency sensitivity with hyper-threading
Primarily like in the TELCO space, they often require increased support for latency sensitive applications. VMware introduced high latency sensitivity in previous releases and in vSphere 8, they are introducing high latency sensitivity with support of hyperthreading. This is designed to support the hyperthreaded workloads and delivered and proved performance for those workloads.
This means, when enabled, Virtual Machine vCPUs are scheduled on the same hyperthreaded physical CPU core rather than being potentially spread across multiple cores. And also, VM requires virtual machine hardware 20.
vSphere with Tanzu VM Consoles
Another improvement in the vSphere Tanzu space is bringing VM consoles to developers. We have deployed virtual machines or cells in the past and for whatever reason we can’t SSH to the VM, we can’t RDP the VM may be something wrong in the network customization. So, what do we do? We open a vSphere client, we pop out the VM console and we are running the virtual machine, and we can troubleshoot and figure out what’s gone wrong.
Now we want to bring that facility to Devops users is well without having to grant them vSphere client access because we want to maintain this separation of role and identity here.
So, now using the kubectl vSphere VM web console command, Devops users that already have current machines on the namespace and current machines on the VMs that they deployed in the namespace can be returned a one-time use of a web console link and they will open this link copied into a browser and they are into their respective machine.
Integrated Skyline Health Diagnostics Plug-in
Another improvement in vSphere 8 update 1 is helping customers adopt VMware Skyline Health Diagnostics. So, now in update 1 there is a guided workflow in vSphere client. It is best feature to know diagnostic issue existing in their environment.
Enhanced vSphere Green Metrics:
In vSphere 8, VMware introduced some metrics to capture power consumption of a host. This included power consumption of virtual machine workloads. But with a totality of all VM workloads on an individual host, we did not have the granularity of a power VM bases.
Using better VM metrics and taking the VM size into the account, we can provide customers more days at aggregate the VM power consumption and better understand the energy efficiency of their workloads.
Elevate Security
- ESXi Quick Boot for Secure Systems
- Quick Boot now supports servers with TPM 2.0
- No longer need to choose between faster patching & host trustworthiness.
vSphere Fault Tolerance with vTPM
Similarly, we had an incompatibility in the areas of vSphere Fault Tolerance and vTPM. vTPM is becoming increasingly important component for guest operating systems now a days, and particularly Windows 11 requires it to be available and it enables things like Microsoft voice guide & credential guide and different OS attestation process and more.
vSphere NFS Datastore VMkernel Binding
Isolating different types of network traffic has always been a best practice and it helps with security and helps the admins diagnose to resolve the admins performance issues since it is very easy to identify or troubleshoot an individual storage interface rather than one that might be shared with other services.
And in vSphere 8 update 1, we are now allowed to bind NFS traffic to individual VM kernel interfaces. So, something that we can do with iSCSI traffic today, bringing that to NFS datastores as well.
vSphere Identity Services
One of the biggest new features in security things in vSphere 8 update 1 is that bringing more modern identity provider support to vSphere. Identity management and multi factor authentication is a big part of security now a days. Adding support for first identity cloud identity provider starting with okta.
We no longer require ADFS, vSphere SSO still available.
Supercharge Workloads
VM DirectPath I/O Hot-Plug
VMware also making an improvement to VMware DirectPath I/O technology. So, typically in the past, if you needed to add a PCI device using VMware DirectPath I/O, it required the virtual machine to be in a powered off state to do the Add and to do the Remove.
In VMware vSphere 8.0 update 1, we have Hot-Add or Hot-Remove NVMe devices using VM DirectPath I/O. There is a specific hardware certification that must support “PCIe Native Surprise Hot Plug” certification. And this designation should appear on the VMware hardware compatibility guide and let us know that the server or the device supports Hot-Add or Hot-Remove using VM Direct Path I/O.
NVIDIA NV Switch
Today many AI and high-performance computing applications need very high bandwidth between multi-GPU applications. And their constraints today by the speeds of things like the PCI express box inside a typical hardware. To solve this, NVIDIA created the special switch called NVSwitch that allows up to 8 GPUs communicate together at 25gbps in each direction or 200gbps in each direction.
So, that’s a huge increasing speed in bi-directional speed from GPU to GPU, much faster than PCI express. Guest OS & Workloads
Virtual Hardware Version 20
For hardware version 20, new innovations have been brought to virtual hardware, improvements have been made to guest services for applications, and performance and scale have been improved. Virtual hardware version 20 is going to be take an advantage of lasts inter and AMD CPU support, Device Virtualization Extensions and up to 32 DirectPath I/O devices.
Deploy Windows 11 at Scale
As we mentioned with that new virtual machine hardware version, new features and functionalities had been added. One of those is the support of additional operating systems including Windows 11. So, enterprises everywhere are sorting to look at how we migrate the Windows 11? How do we use that in VDI infrastructure?
We have the feature that VMware has introduced is virtual TPM (vTPM). We can clone the virtual machine with a TPM device without compromising security.
The problem here is, if we have a Windows 11 machine and want to clone, if we clone that source Windows 11 machine, we are essentially cloning vTPM device along with the TPM secrets. So, that is not a good thing from the security perspective.
So, VMware has introduced “TPM provision policy”. This policy usually clone a Windows 11 machine and it essentially strips out the TPM and it allows us to be re-created with a unique TPM secret for each cloned machine. So, this bounds to security and at the same time it is allowing us to clone those Windows 11 boxes with a vTPM device.
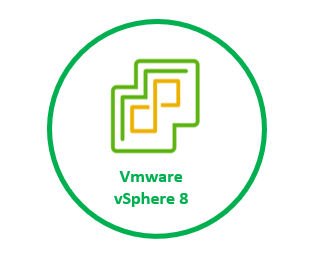
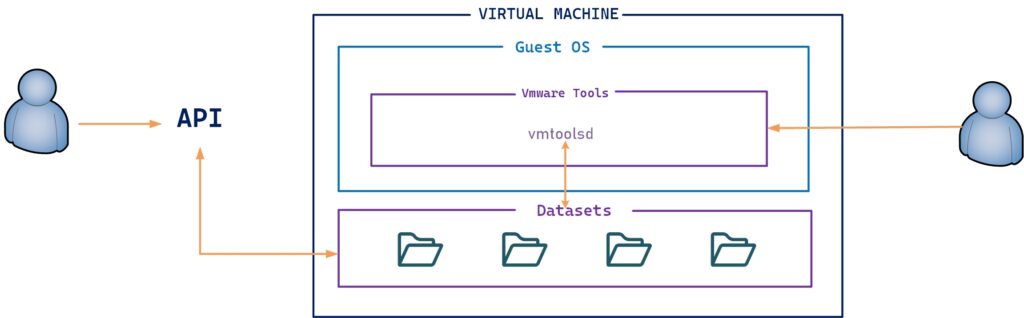
vSphere Dataset’s
vSphere Datasets are a new way through using special APIs that information can be shared between the vSphere management plane as well as the guest operating system.
We have some requirements to use vSphere Dataset’s. VM must be running with VMware Tools and virtual hardware version 20 is required for the VM.
Use cases: Guest deployment status, Guest agent configuration, Guest inventory management.
Device Groups
Device groups allows vSphere to detect and add groups of devices to virtual machines. Currently NICs and GPUs are compatible with this device groups. If you add a device group to the virtual machine, it is nothing, but you added group of hardware.
In the host, device groups may share same PCIe Switch or devices that share a direct interconnect with each other. So, vSphere is going to have that intelligence to manage and present the group of devices to virtual machines.
Data Processing Unit (DPU)
DPUs allow ESXi services to be offloaded to the DPU for increased performance. It is going to be a tremendous savings on resources that can be offloaded from the CPU on to the DPU.
Additionally, when we talk about security having your vSphere management plane is running in a totally separate environment with a DPU as posture running on the CPU where all the virtual machines traffic and the processing is happening, obviously many security ranges to the configuration.
Baseline Lifecycle Management
vSphere lifecycle management has also received new enhancements and updates in VMware vSphere 8.0. As you would have imagined, it had to support many of the architectural changes such as DPU support.
First and fore most, vSphere lifecycle manager can analogs that keep a vSphere installation on your DPU aligned with the installation that is installed on the ESXi host. However, there are also other things to know, as we all expected, vSphere update manager, the baseline configuration that we have used for many versions now has finally received the notice of deprecation.
Another thing to know that they have added with “Cluster remediation”. As you can now stage the updates before you place host in maintenance mode, so its non-disturbed to workloads.
Parallel Cluster Remediation
vSphere lifecycle manager can remediate multiple hosts at the same time. Instead of having a single host go down in maintenance mode migrating workloads, we can now have a parallel update mechanism of those hosts in the cluster so that more hosts can be remediated at the same time.
vSphere Configuration Profiles
Configuration management in your vSphere environment is an important part of overall security and to make sure that all your hosts and clusters are configured consistently and that leads to a better operational experience as well as security. Previously we had to do it with third party tools or scripting using Ansible scripts, power CLI etc., But it is really encouraging with vSphere 8 having vSphere Configuration Profiles.
Migration aware applications
VMware has concentrated efforts on ensuring that applications are not affected by infrastructure operations. And they have created a new concept on vSphere 8, a migration aware vMotion. In another words, if you need to transition a virtual machine to another host, there are steps that we do that more gracefully now at the application level.
Some orchestration is going to be possible with this migration aware of functionality such as stopping services potentially in a guest operating system or performing a failover in the case of a clustered application that’s running inside of those running virtual machine on the top of the VMware vSphere 8.0.
High Latency Sensitivity with Hyper-threading
This allows a virtual machine’s vCPU to be scheduled on the same hyper-threaded physical CPU core. So, there is no disparity between the cores that running on the same physical core and the physical server host. All that helps with ensuring that any latency sensitive applications are unaffected.
Simplified Virtual NUMA Configuration
In VMware vSphere 8.0, VMware is giving the VI admins even more simplified control NUMA nodes. Now, virtual NUMA is extremely important when it comes to performance latency if NUMA is not configured correctly, however, VMware has essentially allowed and exposed in the vSphere Client a simplified virtual NUMA configuration.
So, in VMware vSphere 8.0 with a virtual machine running with hardware version 20, it allows you to essentially use that vSphere Client to configure vNUMA topology for virtual machines.
Another new feature we have underneath the VM summary tab is a new CPU topology attire. What it does is that it gives you a consolidated view of the Cores, the vCPUs, sockets, threads per core and NUMA nodes.
Conclusion:
With the release of VMware vSphere 8.0, many new features and capabilities are available. Furthermore, the upgrade process for vCenter Server is similar to that for previous releases of vSphere. In Previous article discuss about unable to login vCenter server using active directory credentials.
Before upgrading to vCenter Server 8, you must remember a few things. Upgrading straight from vCenter Server 6.5 to 8.0 is not supported. If you have any questions about VMware vSphere 8.0, please leave a comment.