In this article discuss about VMware Virtualization Concept.
In computer world, there are virtual computers. You can’t touch these because they run as a software on a physical machine.
Before understand concept of virtualization, Let’s understand what the physical system configuration is.
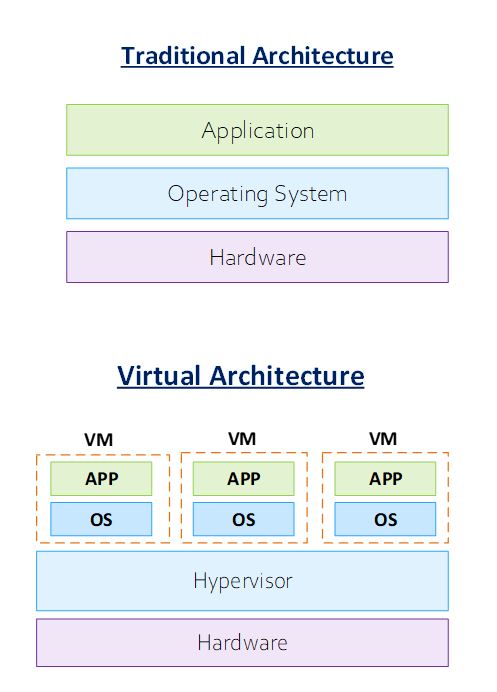
There is a physical server say Dell PowerEdge R750 Rack Server (or) HPE ProLiant DL325 Gen11 top of that Operating system installed example Windows Server Operating System or Linux Operating System. Once Operating System is up and running, then install any application (ex: FTP).
Here the problem with this, suppose you have a physical server with a resource of 16 GB RAM and 4 CPUs, then we go in and install an Operating System, of course the entire resource which is 16GB RAM and 4 CPUs are given to the Operating System. But your Operating System needs just 4 GB RAM and 1 CPU for example, that leaves us 12GB of RAM and 3 CPU. Now, we can install and configure the application.
The application that we are running, for example requires 4 GB RAM and 1 CPU. So, we are left with 8GB and 2CPU remaining in total.
Putting it in other words, 8GB RAM and 2CPUs are underutilized. That is where VMware Virtualization was born. This technology posed as a better way to save the resources and fully utilize those resources, so that we could run multiple applications, we could run multiple Operating System on a same physical server.
We don’t even have to buy more physical server. We can just buy on server and run multiple operating systems on it and then run multiple applications on it. So, that’s where whole VMware Virtualization concept came.
VMware Virtualization
There is a physical server, upon which we install a Virtualization layer say a Virtualization software from VMware, then you install operating systems on it. We can install mutliple Operating System you can, depending on the resources that you have in your physical system. And then on top of those Operating System, you have the application individually to run on each of the operating system.
Now, what is the advantage by using virtualization?
Again, going back to 16gig memory and 4 CPU, the next layer which is the Virtualization layer takes all the 16GB memory and 4 CPUs, then there is OS and applications. Each of the Operating System and application has 4GB of RAM and 1 CPU. Each Operating System are given all the resources. What happens then? All the resources are fully utilized.
That is the beauty of VMware Virtualization. You don’t have to run only one OS at a time. You can run multiple Operating System all at a time. That’s why the virtualization is so important and so beneficial.
In layman terms, Virtualization is a technology used for utilizing a software to create a virtual layer over the single physical hardware which allows for utilizing the system resources and sharing those system resources efficiently among all the operating systems that runs on that single physical server.
Now, we know what Virtualization is. Let’s see how Virtualization exactly works and what is that software that sits on the physical server and make it work.
How VMware Virtualization works
- In virtualization world, that software that sits as a virtualization layer on the top of the physical server is called a hypervisor software. It is a program that is made up of a bunch of codes and programming language. Also, we can say that hypervisor is an operating system of its own. An operating system that is built by the virtualization manufacturer.
- Let’s say we talk about VMWare. It is a cloud computing and virtualization technology company headquartered in California. VMware created a hypervisor that sits on top of the physical server. That Hypervisor is named as ESXi [ Elastic Sky X integrated]
- ESXi allows the communication between the virtualization software and physical server and the communication between the virtual operating system that runs on top of it.
- There are two types of Hypervisors.
- Type -1 / Bare metal hypervisor – This type of hypervisor is built directly on top of the host operating system and utilizes the hardware resources and hence the name bare metal hypervisor. Since, they work directly on hardware, they are highly efficient. Example: VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix XenServer .
- Type -2 / Hosted hypervisor – This type of hypervisor runs as an application on the host operating system. Its co-ordinates with the virtual machine for resource management. It doesn’t directly work on the host Operating System. Example: VMware Fusion, Oracle VirtualBox, Oracle Solaris Zones.
Benefits of VMware:
- Cost Savings – When we think about the fact that we can run multiple virtual environments from one piece of infrastructure, we are drastically reducing the physical infrastructure footprint. We don’t have to maintain as many as servers, run as much electricity and save on maintenance costs. We reduce the chance of buying a new hardware, new resources, new storage, thereby reducing the expenses.
- Resource Efficiency – Before virtualization, each application server used its own hardware resource which were being underused. But with having the multiple virtual machines (VMs), maximum utilization of the hardware capacity occurs, and the resources are being used efficiently.
- Minimum downtime – Downtime refers to the crashes of the OS or the applications which causes halt in the user productivity. Let’s say that one of the hosts goes out unexpectedly, the fact that we can move VM from one server to another is a great back up plan. So, there is almost zero downtime with virtualization.
- Time Management – Buying, installing, and configuring a new system is waste of time. In such case, virtualization can solve the problem, provided the existing hardware resources are sufficient for running the virtualization software. You can deploy a virtual machine just through a template, which is a lot easier and time saving.
- Agility and Speed – Spinning up a virtual machine (VM) is relatively easy and quick, a lot simpler than provisioning an entire new environment. If we must spin up a new environment for testing purpose, patch management etc., virtualization makes the process a lot simpler and quicker. You can always take a snapshot of your machine and revert to it. So that makes the virtualization process agile.
Below are some Top Virtualization Providers:
| Company | Hypervisor | Cloud Technology |
| VMWare | ESXi | vCloud |
| Oracle | OVM / OLVM | OCI |
| Microsoft | Hyper-V | Azure |
| Citrix | Xen server | Citrix cloud services |
| Redhat | KVM | Redhat Cloud Suite |
Basic overview of VMware
- VMware is an American publicly traded software company from California, USA. It provides cloud computing and virtualization software and services. It was the first commercially successful companies to virtualize the x86 architecture in 1998.
- VMware has approximately 85% of the virtualization market share
- There are two virtualization software offered by VMware.
- VMware ESXi – Bare-metal hypervisor that runs over a physical hardware.
- VMware Player – Runs as an application over an already installed operating system.
Products of VMware
- Cloud and Edge Infrastructure – VMware Cloud on AWS, Azure VMware Solution, Google Cloud VMware Engine
- Security & Networking: NSX Advanced Load Balancer, VMware Aria Operations for Networks
- Datacenter & Cloud Infrastructure: VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi), VMware Cloud Director
- Infrastructure & Operations Management: VMware Site Recovery Manager, VMware vRealize Operations Insight, VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service: VMware vCloud Air, VMware Cloud On-Premises Components
- Desktop & End-User Computing: VMware Workstation Player, VMware Horizon
- Endpoint & Workload Security: VMware Carbon Black Cloud Container, VMware Carbon Black Cloud Workload
- Internet of things [IOT]: VMware Internet of things
- VMware Tanzu Data Services: VMware Tanzu SQL with MySQL for Kubernetes, VMware Data Services Manager
Benefits of VMware:
- Security based on a zero-trust model, along with better security than container systems like Kubernetes.
- Better provisioning of applications and resources.
- Simplified data center management.
- Increased efficiency and agility of data center systems.
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi)
The VMware ESXi architecture mainly consists of VMkernel and the processes that run on top of it. VMkernel is technically an operating system. Like other operating systems, VMkernel creates and controls processes, controls hardware devices on the server, uses file system, manages applications resources and so on. However, it’s main function is to support virtual machines. For latest vSphere 8.0 reference VMware Document.
The main processes that run on top of the VMkernel are:
- Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) – It is the low-level configuration and management interface, accessible through the console of the server, used primarily for initial basic configuration.
- Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) – It is the process which provides the execution environment for a virtual machine, as well as a helper process known as VMX. Virtual machines run under their own VMM and VMX processes.
- Common Infrastructure management Model (CIM) – It is the interface that enables hardware-level management from remote applications via a set of standard APIs.
For managing one ESXi host, we require vSphere whereas for managing more than one ESXi hosts, we need VMware vCenter Server.
conclusion:
Take the time to learn more about VMware Virtualization all the points I mentioned in this article. If you have any questions about this topic, please leave a comment.

One thought on “What is VMware Virtualization”