This article defines how to use the Leapp utility to perform an in-place upgrade from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. The existing RHEL 7 operating system is replaced by a RHEL 8 version during the in-place upgrade.
On May 7th, 2019, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 was released. This new release includes numerous new features as well as the option to upgrade from RHEL 7 to RHEL 8.
Requirements
- The system must be running Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 64-bit
- Minimum RHEL 7.6 installed
- If you have the /boot directory on a separate partition, you must have at least 100 MB of free space
- Save routes (route -n) and IPaddress (ip a) configuration details.
- Take a snapshot/backup of the machine.
- If any version lock exists, remove it by running yum versionlock clear
- Make a note of SELinux current status and disable it.
- Disable the firewall.
- Disable root account
Preparing RHEL 7 For the Upgrade
1. Check the machine running on RHEL 7.6, if you are using a version older than RHEL 7.6, you must update your RHEL system to RHEL 7.6 using the yum command below.
yum update
2. To enable system repositories and perform a full system update, ensure that your RHEL 7 system has been successfully registered using the Red Hat Subscription Manager (or) Red Hat Content Delivery Network (CDN).
3. By registering your machine with Red Hat Subscription Management, make sure you have activated RHEL subscription on it.
3. If any external device is connected to your machine remove it
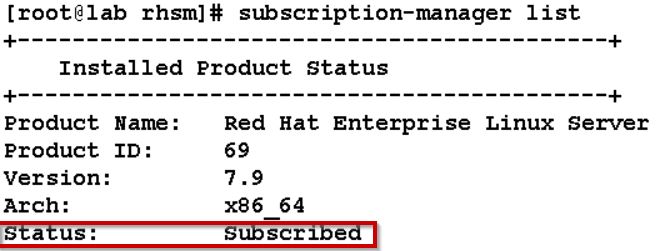
4. Verify that your RHEL 7 system is subscribed to Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server. If not, run the following commands to automatically assign and verify the subscription to the system.
subscription-manager attach --auto
subscription-manager list --installed
5. Using the following command, you can now set RHEL 7.6 as the upgrade’s starting point
subscription-manager release --set 7.6
6. If you used the yum-plugin-version lock plug-in to lock packages to a specific version, run the following command to remove the lock.
yum versionlock clear
7. Verify that the Extras repository must enable for software package dependencies.
Set the Base repository to active
subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-rpms
Activate the Extras repository, which contains Leapp and its dependencies.
subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
Install the Leapp utility
8. Start the pre-upgrade procedure using the leapp preupgrade command to evaluate your system’s upgradeability. The Leapp utility gathers information about the system, evaluates its upgradeability, and produces a pre-upgrade report during this phase.
yum install leapp
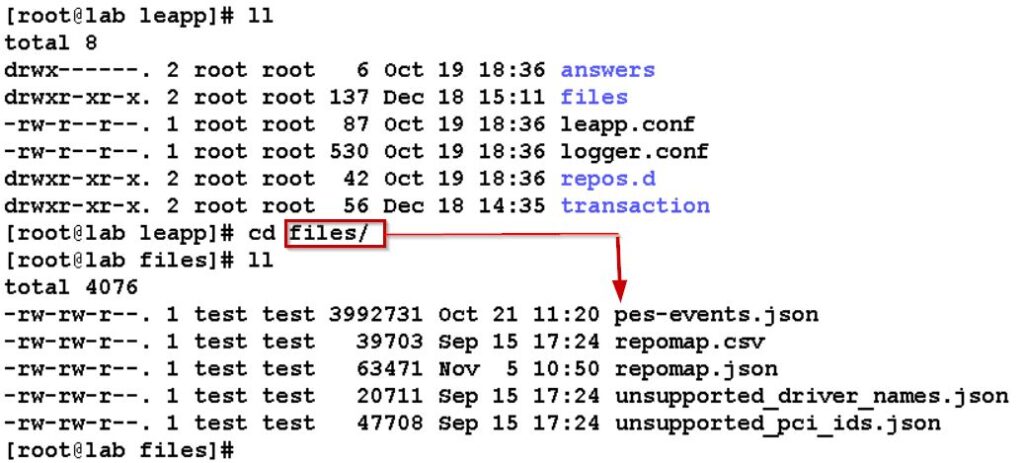
After execution of above command, verify below files must exist in /etc/leapp/files
The pre-upgrade report is available in /var/log/leapp/leapp-report.txt file. The report highlights potential issues and suggests solutions. The report also assists you in determining whether or not to proceed with the upgradations.
Leapp creates true/false questions in specific setups to decide what to do next. All inquiries are recorded in the /var/log/leapp/answerfile as well as in the notification “Missing needed replies in the answer file” in the pre-upgrade report.
NOTE:
If files are not existing, you can manually download Leapp utility from RHEL site under Community Linux distributions will find Zip file called leapp-data15.tar.gz
tar -xzf leapp-data15.tar.gz -C /etc/leapp/files && rm leapp-data15.tar.gz
RHEL 7 to RHEL 8 upgrade
9. Use the following command to launch the RHEL 7 system upgrade procedure
leapp upgrade
10. Typically, you will encounter the following error during the upgrade process
Run below command to fix the issue
leapp answer --section remove_pam_pkcs11_module_check.confirm=True
11. Run again leapp upgrade command, it will work.
It will take around 30-45mints to complete the upgradation. After the upgrades are completed, restart the system manually.
When the update is completed, your homepage should show Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0 (Ootpa). You can see that the kernel has also been updated to 4.18
Post-Upgrade:
- Set back SELinux will be in permissive mode using following command
sed -i 's/SELINUX=permissive/SELINUX=enforcing/g' /etc/selinux/config
- Enable the Firewall Service
systemctl start firewalld
systemctl enable firewalld
- Verify the current operating system version using below command
cat /etc/redhat-release
Conclusion
Completed successfully in-place upgrade from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. Best wishes as you get started with RHEL 8. Please contact me if you need any additional details about the RHEL 7 to RHEL 8 upgrade procedure.
In next article discussed about upgradation procedure from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.