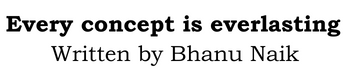In this article, we will examine about ADDC domain could not be contacted.
When you click the Details button to learn more about the error, you will be informed that the DNS name does not exist, as well as an error code. If you’ve encountered the ‘An Active Directory Domain Controller for the domain could not be contacted’ error on Windows, you’re probably not wrong.
Brief information about ADDC domain could not be contacted:
Domain Name System (DNS) name resolution services are used by Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) to assist clients in finding domain controllers and to facilitate communication between domain controllers that host the directory service. For Active Directory functions such as authentication computers use DNS to locate Active Directory domain controllers.
The most common cause of this problem is incorrect configuration of DNS, check ports.
Possible solutions for Active Directory Domain Controller Could Not Be Contacted
Step 1:
- Check DNS settings.
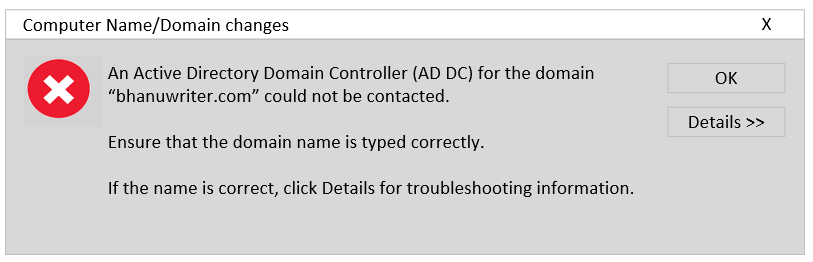
Open command prompt with administrator privileges, type ipconfig /all according to your interface find DNS Servers ip address should exist .If not type ncpa.cpl command in command prompt to check Network Connections Control-Panel Stub file ,right click on interface you can see Networking tab and connection called Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4) select it click on properties enable Use the following DNS server addresses option and provide preferred dns server and alternate dns as shown below.
- When a device makes a DNS request, the preferred DNS servers are selected as the first choice.
The alternative DNS server is only used if the primary DNS server does not respond.
The DNS system relies on them as a backup.
if you have more than 2 DNS servers, click on the Advanced tab, you find the DNS tab click on ADD and enter the IP address. - Now check those ip addresses must be visible in ipconfig /all.
Step 2:
- Ensure the domain controller is reachable and responding.
Open Command as an administrator and check ping <your domain controller ip address> and telnet <domain controller ip address> 53, since Domain Name System (DNS) uses TCP Port 53 for zone transfers. In fact, ping uses the ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) protocol and two types of ICMP – Echo Request and Echo Reply, both must be allowed eventually on a destination machine for a ping to be allowed.
In case ping isn’t working, then you need to run a traceroute command in Command Prompt and send the results to the network team. TRACERT generates echo packets based on Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages sent to a destination to determine its route.
Step 3:
- DNS service
Open services.msc make sure DNS client service status is running.
Ensure that firewalls do not block access to the DNS service on the domain controller. verify by using wf.msc command checks inbound rules and outbound rules.
Step 4
Make sure your computer can figure out the domain name’s IP address. In order to verify open Windows PowerShell and run Resolve-DNSName <your fully qualified domain name (FQDN)>.
join your system to a domain controller, open the command prompt with administrator privileges, run gpupdate /force command to force the update of group policies applied by your domain controller. To make sure all settings are applied, the machine must be rebooted.
Domain Controller to re-register DNS records:
There are two commands that can force a domain controller to re-register its DNS records.
- ipconfig /registerdns: It will register the Domain controller A record.
- net stop netlogon && net start netlogon: It will restart the netlogon service. As soon as netlogon starts, it will attempt to register the rest of the DNS records of the Domain controller.
Conclusion:
Check your machine’s ability to contact the DNS zone’s server to find out the domain and domain controller information, as well as the IP address, by using nltest /dsgetdc:<your fully qualified domain name (FQDN)>.
In my preceding article described the activation of a windows license for a server or client windows machine.
Thanks for reading this article. I hope you find it useful. If you have a question about the ADDC domain that could not be contacted topic, let me know.